Simple Mappings
In our initial example, we already retrieved two STRING fields ... TITLE and ISBN. In both cases, we set a Type of STRING and used a SimpleMapping element to map the SQL name from the result set.
Let's try a DATE field. Enhance your SQL with PUBLISHED_DATE in the SELECT clause as follows:
select TITLE, ISBN, PUBLISHED_DATE from ZBKS_BOOKWe can map this date field to the user interface with a CustomRetrievalField using the DATE type.
<CustomRetrievalField> <FieldRef levelType="Undefined" category="PDF"> <FieldName>Published Date</FieldName> </FieldRef> <Type>DATE</Type> <SimpleMapping sqlName="PUBLISHED_DATE"/></CustomRetrievalField>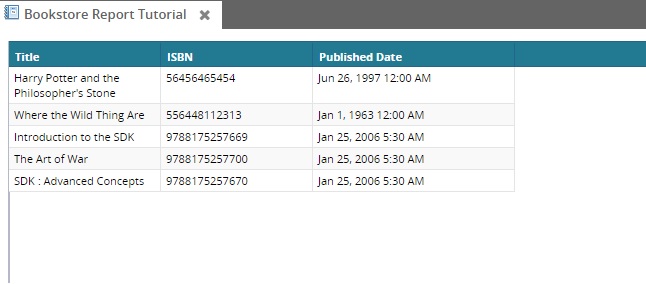
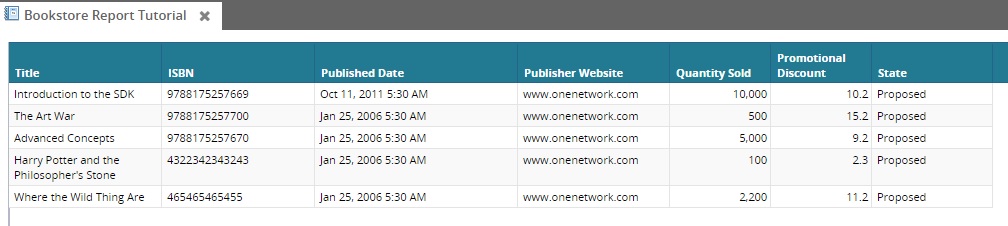
As an exercise, try adding QUANTITY_SOLD (Type INTEGER), PROMOTIONAL_DISCOUNT (Type DOUBLE) and STATE (Type STATE). After adding them, cross-check your solution with the solution provided below:
select TITLE, ISBN, PUBLISHED_DATE, QUANTITY_SOLD, PROMOTIONAL_DISCOUNT, STATEfrom ZBKS_BOOK<CustomRetrievalField> <FieldRef levelType="Undefined" category="PDF"> <FieldName>Quantity Sold</FieldName> </FieldRef> <Type>INTEGER</Type> <SimpleMapping sqlName="QUANTITY_SOLD"/></CustomRetrievalField><CustomRetrievalField> <FieldRef levelType="Undefined" category="PDF"> <FieldName>Promotional Discount</FieldName> </FieldRef> <Type>DOUBLE</Type> <SimpleMapping sqlName="PROMOTIONAL_DISCOUNT"/></CustomRetrievalField><CustomRetrievalField> <FieldRef levelType="Undefined" category="PDF"> <FieldName>State</FieldName> </FieldRef> <Type>STATE</Type> <SimpleMapping sqlName="STATE"/></CustomRetrievalField>